By Ryan Leasure
This article is part four in a nine-part series on how we got the Bible. Part 1 looked at biblical inspiration and inerrancy. Part 2 considered the development of the Old Testament. And Part 3 investigated the Old Testament canon and the Apocrypha.
In this article, we transition to the New Testament canon. Specifically, I want to answer two questions. First, would the first-century Christians have expected new Scripture in addition to the Old Testament? And second, what attributes did the church look for in canonical texts?
Would the First-Century Church have Expected New Scripture?
Biblical scholar Harry Gamble once remarked, “There is no intimation at all that the early church entertained the idea of Christian scriptures… Therefore, the NT as we think of it was utterly remote from the minds of the first generation of Christian believers.”1. What are we to make of Gamble’s assertion? Was he right? Did the early church assume that God was done inspiring Scripture after the close of the Old Testament? I believe we have good reason to reject Gamble’s claims. Let me give you three reasons why.2
1. First-century Jews regarded the Old Testament story as Incomplete
Several texts from the Gospels and Acts demonstrate that first-century Jews expected God to do something in their generation. Not only were they on the look-out for the Messiah (Luke 2:38; 2:25; John 1:41; 4:25), they expected God to usher in his kingdom and overthrow their oppressors (Acts 1:6; see Dan 2:31-45). Second Temple period (intertestamental) texts also confirm this same expectation (Tob 14:5-7; Bar 3:6-8). As N. T. Wright notes, “The great story of the Hebrew scriptures was therefore inevitably read in the Second Temple period as a story in search of a conclusion.”3
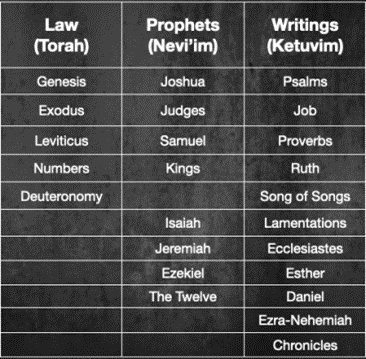
The close of the Old Testament also gives the impression that the Jews expected a Davidic King to rise up among their ranks. Keep in mind, according to Jewish ordering, Chronicles was the final book of the Old Testament. And that book starts off with a lengthy genealogy centered around King David (1 Chron 1-3). It’s no coincidence that the start of the New Testament picks up right where the Old Testament left off with a genealogy focusing on the Son of David (Matt 1). It’s as if the Gospel of Matthew brings the story of the Old Testament to its necessary fulfillment.
2. God’s Pattern of Bringing New Word-Revelation after his Acts of Redemption
According to the Old Testament pattern, God typically gives revelation deposits after his redemptive acts. We see this sequential pattern most clearly in the Exodus. God redeemed his people out of Egypt. He then followed up that redemption with Scriptural installments at Sinai to interpret his saving acts. Given this history, it’s not inconceivable that the early church would have expected more written revelation following Jesus’ act of redemption.
3. The Old Testament Predicted that the Future Messianic Age would Include Verbal Communication
Not only did the Old Testament predict a future messianic age, it predicted that communication would accompany the Messiah. Deuteronomy 18:18 predicts “I will raise up for them a prophet like you from among their brothers. And I will put my words in his mouth, and he shall speak to them all that I command him.” Isaiah 61:1-2 says of the Messiah that “The Spirit of the LORD God . . . has anointed me to bring good news to the poor . . . to proclaim liberty to the captives . . . to proclaim the year of the Lord’s favor.” And of this Messianic age, we read, “out of Zion shall go the law, and the word of the LORD from Jerusalem” (Isa 2:2-3).
In sum, those living after the close of the Old Testament recognized that the story was incomplete, that God typically gave word-revelation following his redemptive acts, and that the Old Testament anticipated a verbal Messianic age.
What Attributes did the Early Church Look for in a Canonical Text?
Now that we’ve established the early church’s expectation for more biblical texts, we must now ask what attributes they would have looked for in those new biblical texts. In the remaining space, I will consider three of these attributes—apostolic authority, marks of inspiration, and universal reception.4 Let’s consider each canonical attribute in turn.
Apostolic Authority
Going back to the New Testament, the apostles recognized that they were “ministers of the New Covenant” (2 Cor 3:6), and that the church was “built on the foundation of the apostles and prophets (Eph 2:20). They also recognized that Jesus had sent them out as the guarantors and transmitters of his message to the world (John 20:21). For these reasons, the early church only received texts that could be traced back to an apostle.
Therefore, from an early time, the church received the four Gospels, Acts, and Paul’s letters. Of course, Paul makes his apostolic authority known in his letters, but the Gospels make no such claim. How then did they receive apostolic status at such an early stage in the church?
Critics argue that since the authors don’t mention their names in the body of the text, the Gospels must have been originally anonymous. It was only after some time that the church added titles to give these anonymous works some needed credibility. Yet, the critics’ assertions lack evidence. All the earliest manuscripts with titles list Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John as the authors. Additionally, numerous church fathers state unequivocally that Mark wrote his Gospel based on Peter’s eyewitness testimony, and that Matthew, Luke, and John all wrote their respective Gospels.
That said, why did the church receive Mark and Luke if they weren’t apostles themselves? It’s because of their close association with the apostles. That is to say, books with apostolic authority were not limited to books that were written by the apostles. Rather, books that came from apostolic circles also came with apostolic authority. Notice Tertullian’s comment about Gospel authorship: “Of the apostles, therefore, John and Matthew first install faith into us; whilst of apostolic men, Luke and Mark renew it afterwards.”5 Tertullian affirms that Mark and Luke were “apostolic men” by nature of their close association with the apostles Peter and Paul.
This close proximity to the apostles also explain why Hebrews made its way into the canon. The author indicates he knew Timothy (Heb 13:23) and that the Gospel message “was declared at first by the Lord, and it was attested to us by those who heard” (Heb 2:3). These two texts combined indicate that the author walked in apostolic circles (probably Pauline), and therefore, his book was apostolic.
Jesus’ family (James and Jude) also received quasi-apostolic status as well based on their relationship to the Lord. We don’t know as much about Jude, but we know James became a prominent leader in the Jerusalem church and later martyr for his Christian faith.
At the same time, the church rejected books from non-apostolic sources. Commenting on the so-called Gospel of Peter, church father Serapion declared, “We receive both Peter and the other apostles as Christ, but the writers which falsely bear their names we reject.“6 Serapion asserted that the church should reject the heretical Gospel of Peter and all others that falsely bear the apostles’ names (Thomas, Philip, etc.).
The Muratorian Fragment makes a similar comment around AD 180. It notes, “There is said to be another letter in Paul’s name to the Laodiceans, and another to the Alexandrines, both forged in accordance with Marcion’s heresy, and many others which cannot be received into the catholic church, since it is not fitting that poison should be mixed with honey.”7 Again, the church rejected all forgeries. The fragment also notes that the beloved Shepherd of Hermes should not receive canonical status because it was written “quite recently, in our own times.” In other words, someone wrote this book after all the apostles had died out.
Marks of Inspiration
Second, the church looked for books that possessed marks of inspiration. If a book came from God, one would expect it to reflect God’s nature and other previously inspired texts. The text, therefore, should reflect the beauty and excellence of God (Psalm 19:7-10). As Jerome once remarked about a New Testament text, it is a “document which has in it so much the beauty of the Gospel,” which is the “mark of its inspiration.”8
Moreover, the text will be accompanied with transformative power. In other words, the text isn’t just words on a page. The text is “living and active” (Heb 4:12). Justin Martyr remarked, “For they possess a terrible power in themselves, and are sufficient to inspire those who turn aside from the path of rectitude with awe; while the sweetest rest is afforded to those who make a diligent practice of them.”9 Irenaeus also asserted that the Gospels are always “breathing out immortality on every side and vivifying men afresh.”10 That is to say, the early church recognized that certain texts brought about salvation and good works in the life of the church.
Not only will the text possess a certain beauty and power, it will be harmonious with other authoritative Scripture. For this reason, the church rejected books like 2 Maccabees which suggests we can offer sacrifices and prayers for the dead (2 Macc 12:43-46). They also rejected gnostic texts (Gospel of Philip, Gospel of Truth, Gospel of Peter, etc.) because they undermined the entire Old Testament altogether. And they rejected the Gospel of Thomas which has Jesus saying, “Look, I will guide her (Mary) to make her male, so that she too may become a living spirit resembling you males. For every female who makes herself male will enter the kingdom of Heaven”—a clear repudiation of Genesis 1-2.
Thus, as Irenaeus remarked, “All Scripture, which has been given to us by God, shall be found by us perfectly consistent.”11. And as Justin Martyr declared, “I am entirely convinced that no Scripture contradicts another.”12
In short, the church only received texts which bore the marks of divine inspiration. These marks included a certain beauty, power, and harmony, indicating that God was their ultimate author.
Universal Reception
Finally, only books that were universally received by the church obtained canonical status. This means that books like 1 Enoch, which only a few small churches received, did not receive authoritative status. After all, Jesus says, “My sheep hear my voice, and I know them, and they follow me” (John 10:27). Therefore, we could expect the universal church to come to some sort of consensus when it came to their Scriptural texts. And this is exactly what we find in the early church.
From as early as the second century, the church recognized a core group of canonical books which included the four Gospels, Acts, Paul’s letters, Hebrews, 1 John, 1 Peter, and Revelation. This consensus is reflected in several church Fathers (Irenaeus, Origen, Clement of Alexandria, Tertullian) as well as the Muratorian Canon. By the fourth century, the remaining fringes of the canon were universally recognizes as reflected in Eusebius (AD 325), Athanasius (AD 367), and the Councils of Hippo (AD 393) and Carthage (AD 397).
A Canonical Grid
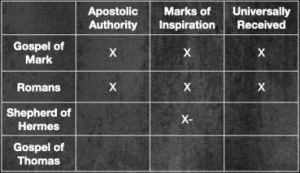
As one considers the three canonical attributes, it becomes clear that the early church filtered books through a sort of canonical grid to help them recognize authoritative texts. Only books possessing all three attributes achieved canonical status. Consider the following chart. Notice how both Mark and Romans possess all three attributes while the Gospel of Thomas possesses none. Also notice that the Shepherd of Hermes partially possesses one of the attributes insofar that it is an orthodox text. That said, it lacks the other two attributes:
Recommended resources related to the topic:
Cold-Case Christianity: A Homicide Detective Investigates the Claims of the Gospels by J. Warner Wallace (Book)
Why We Know the New Testament Writers Told the Truth by Frank Turek (mp4 Download)
The Top Ten Reasons We Know the NT Writers Told the Truth mp3 by Frank Turek
Counter Culture Christian: Is the Bible True? by Frank Turek (Mp3), (Mp4), and (DVD)
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Ryan Leasure holds a Master of Arts from Furman University and a Masters of Divinity from the Southern Baptist Theological Seminary. Currently, he’s a Doctor of Ministry candidate at the Southern Baptist Theological Seminary. He also serves as a pastor at Grace Bible Church in Moore, SC.
Original Blog Source: https://cutt.ly/1Ouq929