By Josh Klein
Lil Nas X
Do you know the name? I do not know why you would, but Lil Nas X has become a bit of a cultural icon in recent years. He wrote a hit country/hip-hop song in 2019 called “Old Town Road” with country star Billy Ray Cyrus. The success of the hit propelled Lil Nas X into the modern spotlight. The song, and its remix, won him fourteen awards spanning from the Grammys to Kids’ Choice Awards[1].
As a result, Lil Nas X toured the country singing for elementary-age kids and was even quoted as saying young kids were his “core audience”[2] in early 2021.
Why am I writing about Lil Nas X on a Christian website?
Well, this man that vies for the eyes and ears of children recently released a new music video that is anything but “kid-friendly.” In his song Montero, Lil Nas X is seen flirting with the Devil, having the Devil lick his navel, pole dancing to Hell, and then giving Satan a lap dance in the underworld. At the end of the clip, Lil Nas X breaks Satan’s neck and removes his crown, declaring himself the king of Hell (which we know is inaccurate, theologically speaking… Satan does not rule Hell – see Rescuing Hell).
To capitalize off the viral video’s success, Lil Nas X also teamed up with a branding company called MSCHF (a play on the word mischief) to release a pair of Nike-branded shoes (Nike has since sued MSCHF for copyright infringement) dedicated to Satan[3].
Lil Nas X also happens to be a gay man. Which would not even be on the top list of problems with the aforementioned publicity stunt, but since Lil Nas X used his upbringing as a catalyst for the release of the new song and video, it is pertinent to the conversation[4].
This article, though, is not about Lil Nas X, or Satan shoes, or the increasing leftist dogma being thrust upon our children.
I wanted to look at the core issue around Lil Nas X’s song, and a core issue going on in Evangelical circles for the past decade-plus.
Homosexuality.
A few weeks ago, I got a text from a young person concerning this very subject:
“I want to do research into God’s view on homosexuality because I’ve been seeing a lot of different takes on TikTok and Instagram and such but it could be heresy or misinterpretation or something else and I want to find out for myself.”
In Sean and Josh McDowell’s book The Beauty of Intolerance[5], the two seek to tackle the issue of Truth and Love and use the example of a family’s argument about sexuality as the impetus for such a discussion. If you have not read the book, it is a good read and gets to the point of the current culture of a new tolerance that seeks compliance, rather than acceptance, to a narrative of subjective moral values.
But the argument on homosexuality within the Church goes back decades, so what is new? The newness of the issues stems from a poor approach to the issue of homosexuality in the 1970s-1990s from the conservative evangelical Church. Homosexuality was rarely talked about and was often seen as a political issue more than a sin issue. I highlight some of this in a previous article on Free Thinking Ministry’s website[6] (Cuties article) so I won’t go into all of the history here.
However, I think it is important to note that the argument that Christians got lost on during that time was whether or not Homosexuality was a choice or genetic.
The argument goes that if it was a choice, we could reform the homosexual; but if it was genetic, then we could not. This argument also implies that natural proclivity could equate to God-ordained behavior.
I remember growing up in the ‘90s hearing many evangelicals talk like it was absolutely imperative that no “gay gene” would ever be found. Almost as if that scientific discovery would shatter thousands of years of orthodoxy on the topic.
But the biblical case against homosexual behavior is not genetic.
It is spiritual and biblical.
Genetics are just as affected by the fall as our spiritual state, and we know this. When we say things like “in the end, there will be no more sickness or death,” we are not just referring to scripture (Rev. 21:4) but we are affirming that there is a physical component to the fallen nature of man. In other words: Our DNA, physical dispositions, and natural proclivities are fallen just as our soul is fallen.
I want to be clear, I am not calling homosexuality a sickness, at least not a mental illness anyway. But it, like many other “dispositional sins” is a sickness of the soul.
Homosexuality is a product of the fall[7] just as much as lying, cheating, or heterosexual promiscuity. Whether or not it is natural is of no relevance to the theological topic. There are many natural behaviors that we are called to curb as Christians. Covetousness, lust, greed, and pride are just a few of many natural proclivities that human beings are born with that must be dealt with overtime in the sanctification process of the Christian.
Homosexuality falls in line with many of those natural proclivity sins. The church argued against genetics when it never needed to, and as it argued against genetics it allowed a narrative of identity to undercut the nature of the issue.
And now we have a bigger problem.
No longer are we speaking to the activity, we are speaking to a person, and in their minds, we are asking them not to be themselves. We are telling them to release, not only a proclivity of human nature but their entire identity of belonging.
In a sense, we are telling them to call themselves evil.
But no Christian worth his/her theological salt would state that being gay condemns a person to Hell. No, we are not sinners because we sin, we sin because we are constituted sinners, and thus, we stand condemned already (John 3:17). In a sense, it is not sin that makes us evil but our evil hearts that make us sin. God rescues us from our already moribund disposition. We are all basically bad and we all need a new identity to overcome this badness.
However, one can see why someone that identifies with being a homosexual would find it hard to follow a God that calls what they think is their defining nature a sin. If a person is basically good, then their core identity is also basically good.
But orthodox Christian doctrine teaches, and rightfully and logically so, that we are all basically bad and in need of saving. Our identity then is sin and we need an exchange of identity to be good! All of us.
Orthodox theology, to the LGBTQ+ people, screams that God made a mistake when He made them. And like Lil Nas X, they either hate themselves or rebel against the faith altogether:
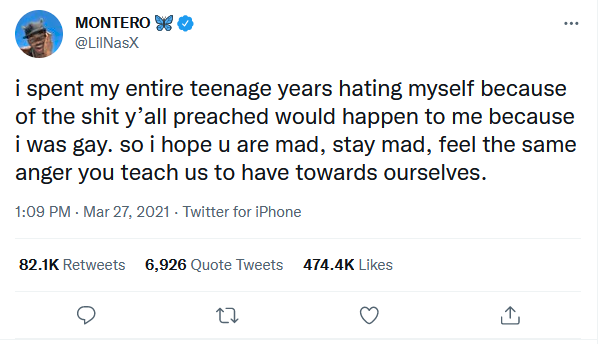
The result of preaching behavioral modification instead of identity transformation is self-loathing and angst, not a conviction.
The natural result of this, then, is to capitulate to the offended; and the liberal theological movement sought to do just that. They sought to provide a theological landing spot for hurting homosexuals in the body of Christ.
God is love, and as a result, He would not want anyone hating themselves because of their identity. So, we must augment our hamartiology (the study of sin) to allow for behavior that was understood to be sinful over the history of the church because God does not make mistakes.
It is true that God does not make mistakes, but it is not true that His creation right now is perfected. Thus, we are inherently flawed and sinful. If we were not, why would we need a savior at all?
The mistake the liberal theologians make is to assume that there is any room for an identity other than “child of God”[8].
I am a man that is attracted to the opposite sex, but my identity is not wrapped up in that attraction.
My identity is either a sinner or saint. Blessed by God to be invited into His family, I can declare that I am a child of God that happens to be attracted to women. However, as a result, that natural proclivity of attraction must be curbed to reflect God’s design.
One woman for a lifetime.
I have embraced this limitation joyfully, because it is no limitation at all, but is a realization of the freedom found in the Godhead through Christ. And I believe, firmly, that those who are homosexuals can experience this same counter-intuitive freedom. More on that in the next few weeks.
The response to homosexuality in that regard should be simple enough. You can be a man or woman that happens to be attracted to the same sex (regardless of if it is a choice or is a genetic disposition) but if you are a child of God (believer in Jesus as your Savior) then that proclivity of attraction must be curbed to reflect God’s design.
Which, unfortunately for the person with natural homosexual proclivities, would be self-denial of acting on that attraction.
My heart aches for this person in a very real way and my empathy extends to them in more ways than they know. But the truth is the truth, and sin is sin. There is no such thing as having compassion on a lie, for entertaining a lie and letting it live is neither compassionate nor merciful. True compassion is lovingly, but firmly, confronting sin and falsehood in the name of Christ and offering freedom in His name.
Just as any heterosexual man that has struggled with pornography will attest, this self-denial of sexual pleasure is beyond difficult and nothing to be glossed over. But we do not deny sexual pleasure to punish ourselves, we do so to glorify God. Boundaries are not set to avoid Hell, they are set to glorify heaven. When we make the mistake of setting boundaries around sin to avoid sin instead of to glorify God we set ourselves, and others, up for fantastic failure.
And it is when we do this that we are tempted to empathize with the seemingly unwinnable battle. I have empathy for all who fight to avoid sin. I know how hard that is, but misplaced empathy can lead to a dangerous theological road and that is what we will tackle next week. How do we show empathy but hold fast to the truth? For that is true mercy and compassion. And that is the mission of the Christian.
Footnotes
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_awards_and_nominations_received_by_Lil_Nas_X
[2] https://www.gpb.org/news/2021/01/06/lil-nas-x-says-children-are-his-core-audience-right-now-and-thats-ok
[3] https://satan.shoes/
[4] https://www.nbcnews.com/think/opinion/lil-nas-x-s-satan-shoes-trolled-some-christians-montero-ncna1262495
[5] https://www.amazon.com/Beauty-Intolerance-Setting-Generation-Truth-ebook/dp/B015F06DMS
[6] https://freethinkingministries.com/cuties-the-natural-progression-of-love-is-love/
[7] https://biblia.com/bible/esv/romans/1/26-27
[8] https://www.biblegateway.com/passage/?search=1+John+3%3A1&version=NASB1995
Recommended resources related to the topic:
Five Questions No One Ever Asks About Gay Rights (DVD Set), (Mp4 Download), and (Mp3 Set) by Dr. Frank Turek
Correct, NOT Politically Correct: How Same-Sex Marriage Hurts Everyone (Updated/Expanded) downloadable pdf, PowerPoint by Dr. Frank Turek
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Josh Klein is a Pastor from Omaha, Nebraska with 12 years of ministry experience. He graduated with an MDiv in 2016 from Sioux Falls Seminary and spends his spare time reading and engaging with current and past theological and cultural issues. He has been married for 12 years to Sharalee Klein and they have three young children.
Original Blog Source: https://cutt.ly/nEESkRX











