“The fine structure constant could easily be larger, the photon massive, quarks heavier, or even worse, electrons, photons, or quarks might not [exist] .. Any one of these would be enough to eliminate our presence.[1]” Physicist Leonard Susskind
This blog is yet another installment in a series on how the fine-tuning of the universe for life provides evidence for God. Here are other blogs in the series:
Intro/Philosophical Background
If You Don’t Want God, You Better Have a Multiverse!
How Does Fine-tuning Provide Evidence for God?
Objections
Mistaken Objections that Seek to Trivialize Fine-Tuning
Important Objections in the Fine-Tuning Debate
Evidence
Fine-Tuning of Initial Conditions to Support Life
Many Changes to the Laws of Physics Would be Life-Prohibiting
Fine-Tuning of the Force Strengths to Permit Life
This blog examines how hard it is to get the right type of building blocks to support intelligent life. Not just any types of particles suffice – no scientist speculates about photon-based life or neutrino-based life since there would be no way to store or replicate information[2]. Consider that every second you have about 65 billion neutrinos passing through the tip of your finger, and at night solar neutrinos travel unaffected through the entire earth before going through your fingertip. The only plausible forms of advanced life that could originate anywhere in the universe are based on atoms. You might think that the mass of a particle doesn’t really matter that much. It’s easy to envision ourselves being composed of protons or electrons or quarks of a different mass. But this turns out to be quite mistaken. The mass of particles is very important in determining their longevity, their suitability in sustaining nuclear reactions in stars, and their suitability for chemistry. In this blog, I’ll once again be extensively utilizing Luke Barnes excellent fine-tuning article as a resource, but I’ll also refer to writings of leading physicists such as Leonard Susskind, Stephen Hawking and Nobel Prize winner Frank Wilczek.
In order to have evidence that life-permitting physics is a small subset among possibilities we must have some idea of the range of possibilities. In this context, we’re on pretty firm ground. There is a maximum mass for particles as set by the Planck scale. The current concept of mass would become incoherent if particles could exceed the so-called Planck mass. The Standard Model provides a means of computing quantum corrections that affect masses, resulting in a natural scale for particle masses. Let’s examine whether or not the mass of certain particles has to be finely-tuned to support life.
The Masses of the Electron and the Proton
“If protons were 0.2 percent heavier, they would decay into neutrons, destabilizing atoms.[3]” Hawking in Grand Design
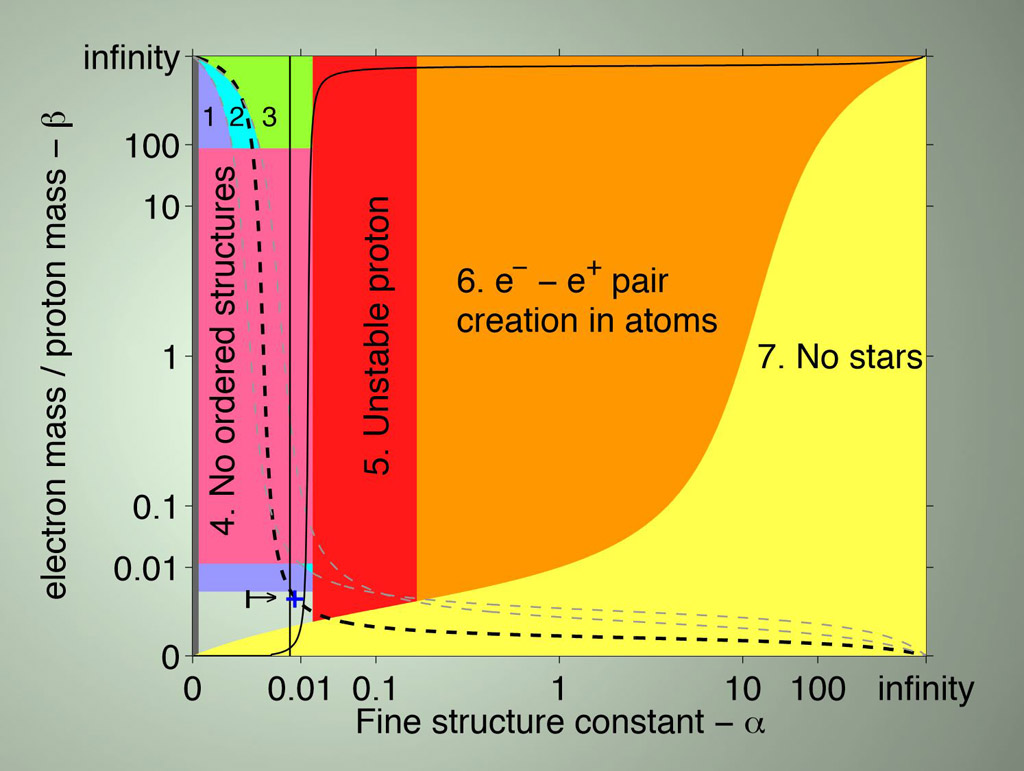
For this data, I’d like to show you a graph from Barnes’s review article[4] with notes about the various life-permitting constraints.
Credit: Luke Barnes Review Article
Notes About Diagram: The graph’s axes are scaled based on arctan(log10[x]) such that [0,∞] maps to a finite range. Refer to my previous blog for a more detailed explanation of coupling constants but basically these are just the dimensionless fundamental constants that convey the strength of the fundamental forces. Here is some notation used in the descriptions of the life-permitting criteria:
α – the electromagnetic coupling constant (also referred to as the fine-structure constant)
αs – the coupling constant for the strong nuclear force
β – the ratio of the mass of an electron to the mass of a proton
The tiny life-permitting region has to simultaneous satisfy each of the following life-permitting criteria and our universe’s values are at the ‘+’ sign near the lower left:
1) For hydrogen to exist the mass of an electron must be less than the difference in the masses of a neutron and a proton else the electron would be captured by the proton to form a neutron. Without hydrogen, there would be no water and no long-lived stars (e.g. Helium stars burn out 30 times faster).
2) Atoms are only stable if radius of an electron orbit is significantly greater than the size of the nucleus – this depends on the ratio of the electron and proton masses such that αβ/αs < 1/1000.
3) The energy scale for chemical reactions should be much smaller than that for nuclear reactions. Otherwise, information could not be stably stored because the type of elements in molecules would be changing because chemical identity would not be maintained. This requires the ratio of the electron and proton masses to be finely-tuned such that α2β/αs2 < 1/1000.
4) Unless the fourth root of β is less than about 1/3, molecular structures would be unstable. They would basically be continually melting and thus disrupting the ability to store information.
5) The stability of the proton requires the electromagnetic coupling constant to be less than the difference of the masses of the down quark and up quark divided by a constant. This enables the extra electromagnetic mass-energy of a proton relative to a neutron to be counter-balanced by the bare quark masses.
6) This fine-tuning is related to the electromagnetic coupling constant and was covered in my previous blog.
7) Stars will not be stable unless β > 0.01 α2
Note that life-permitting criteria 2-5 and 7 also depend on one or more coupling constants and thus reinforces my previous arguments about the difficulties in getting simultaneous solutions to so many independent equations. There are also some additional constraints on the masses of the proton and electron not necessarily shown in Barnes’s diagram:
- A constraint on the main nuclear reaction in stars. This depends on a finely-tuned strong nuclear force strength as previously mentioned but also depends on a particular relationship of the masses of the up and down quarks and the electron.
- The ratio of the mass of the electron to the proton also affects the ability of stars to output photons at energy levels that break chemical bonds (this was also referenced in my previous blog because it also depended on force strengths). The dashed line in the diagram represents that constraint.
- The mass of the electron and proton also show up in the equation for the cosmological parameter Q as described in my previous blog.
These tight constraints on the life-permitting region for the mass of the electron are even more surprising because the values are deemed “unnaturally low” to begin with. Barnes elucidates this issue: “There are, then, two independent ways in which the masses of the basic constituents of matter are surprisingly small … the Hierarchy Problem … and the flavour problem. … The electron mass is unnaturally smaller than its (unnaturally small) natural scale set by the Higgs condensate.[5]” These are called problems simply because they require fine-tuning – the values they take on are quite different than the natural scale. It’s possible that new physics discoveries might minimize the unnaturalness somewhat but the life-permitting ranges are so tight that there is no basis for assuming that the fine-tuning will go away.
There is also a tight constraint on the charge of the electron. The electromagnetic coupling constant can be expressed in terms of a ratio involving the square of the charge of an electron. Thus, the numerous constraints referenced in my previous blog can also be viewed as a dependence on the charge of the electron. Thus, consider again the fine-tuning necessary for the production of carbon and oxygen in stars. This required fine-tuning of the electromagnetic coupling constant to 1 part in 10,000. Thus, another way of looking at this is that if the electron differed in charge by more than 1 part in 100,000,000 in either direction then the universe would basically be devoid of carbon or oxygen or both.
In order to understand more details about the mass of the proton, a little background will be helpful. A proton is comprised of 2 up quarks and a down quark and a neutron is comprised of 2 down quarks and an up quark. Most of the mass of these composite particles is derived not from the quarks but from the energy due to the strong force that is constraining them. This binding energy is equivalent to mass as per Einstein’s famous equation: E=mc2. Thus, we should also examine the sensitivity of the quark masses.
Quark Masses
“[T]he up- and down-quarks are absurdly light. The fact that they are roughly twenty thousand times lighter than particles like the Z-boson . . . needs an explanation. The Standard Model has not provided one. Thus, we can ask what the world would be like if the up- and down-quarks were much heavier than they are. Once again – disaster![6]” Leonard Susskind
The mass of the quarks is derived from the Higgs boson but the other approximately 98% of the proton and neutron mass is based on the binding energy of the strong nuclear force. Quark masses vary from roughly 10 to 344,000 times the mass of the electron and thus if the masses of the up and down quarks only support life within narrow ranges relative to possible quark masses, this constitutes a high degree of fine-tuning. Research into the physics literature reveals very widespread agreement that these quark masses are finely-tuned. Barnes cites at least 7 physics articles arguing for this conclusion. Physicist Craig Hogan affirms this conclusion: “Changing the quark masses even a small amount has drastic consequences for which no amount of Darwinian selection can compensate.” Hogan reminds us that fine-tuning deals with what has to happen before any biological evolution could get started.
Barr and Khan’s article considers the 60+ orders of magnitude in the space of possible up and down quark masses and document 9 different life-permitting criteria that end up constraining the life-permitting region to a tiny subset in the space of possibilities. I conservatively measured the improbability off their graph as no more than 3 parts in 1036 – this makes it less likely than picking out one red grain of sand in a giant sand pile in Eurasia up to the height of the moon (to harken back to my analogy from a previous blog).
Most of these criteria are very clear cut disasters for life of any kind – for example there are constraints necessary to have stable protons, neutrons and atoms, and there are a couple of disasters where only one type of long-lived particle would exist with the chemistry of either hydrogen or helium.
Other particles
“Atoms, molecules and life are entirely dependent on the curious fact that the photon has no mass.[7]” Susskind
Susskind goes on to explain that no life could exist if the photon had even a tiny mass because otherwise electromagnetic force acts at too limited of a range for chemistry to be operative. The Higgs Boson has been in the news lately since it was discovered recently at the LHC. Luke Barnes documents how, in natural Planck units, the vacuum expectation value of the Higgs Boson must be between 4e-17 and 2e-14. He cites 4 different articles and multiple finely-tuned criteria.[8]
Even the mass of neutrinos turns out to require fine-tuning to support life. Tegmark, Vilenking and Pogosian argue that if the sum of the mass of the 3 species exceeds just 1 electron volt then no galaxies would exist. They refer to this as an anthropic constraint so they seem convinced that life couldn’t form if there were no galaxies, presumably since galaxies are critical for star formation. This constraint is significant since neutrino masses are so tiny compared to other particles. For example, the top quark is 170 billion times more massive than this!
Will New Physics Rescue Us From the Need for All of These Fine-Tunings?
Physicist Craig Hogan argues that the “two light quark masses and one coupling constant are ultimately determined even in the `Final Theory’ by a choice from a large or continuous ensemble… the correct unification scheme will not allow calculation of [the masses of the proton and the up and down quarks] from first principles alone.” So these parameters have a large range of choices and a small life-permitting range and there is no good reason to expect a ‘Theory of Everything’ to force these masses to their current values. We should remember that even if this were the case, there would still be a fine-tuning argument based on what is metaphysically possible. Physicists would still be astounded at the coincidences: “Even if all apparently anthropic coincidences could be explained [in terms of a more fundamental theory], it would still be remarkable that the relationships dictated by physical theory happened also to be those propitious for life.[9]” Bernard Carr and Sir Martin Rees
Actually, grand unified field theories and other new more fundamental physics theories introduce new fine-tuning requirements. Most of these theories assume something called supersymmetry is true. However, if supersymmetry were true at our energy scales, there would be no life anywhere in the universe as Susskind has pointed out[10]. In this unconfirmed theory, every particle has a partner particle of the opposite type – bosons have partners that are fermions and vice versa. Thankfully, even if supersymmetry turns out to be true, it’s a broken symmetry at low-energies! Barnes also points out that the Grand Unified Theories provide “tightest anthropic bounds on the fine structure constant, associated with the decay of the proton into a positron and the requirement of grand unification below the Planck scale.[11]” So these new candidate theories do not eliminate fine-tuning.
If you’ve been following my fine-tuning blog series, I hope by now you see the incestuous nature of the inter-dependencies and inter-connections of finely-tuned parameters and how incredible it is that there is a solution to all of the concurrent equations that must satisfy multiple, entirely independent life-permitting constraints. Consider that if you have 10 linear equations and 10 “unknown” variables then there is usually at least 1 solution to all of the equations. This becomes increasingly unlikely is as you add non-linear terms or as you reduce the number of variables. Thus, if new physics reduces the number of variables (the fundamental constants) that makes it more surprising that a simultaneous solution exists to all of the life-permitting criteria!
Can the Multiverse Explain this Fine-Tuning?
Recall our discussion about how the multiverse, if it is to explain fine-tuning, predicts that the fine-tuning will be barely enough to be life-permitting. As physicist Paul Davies notes: “there is no a priori reason why the laws of physics should be more bio-friendly than is strictly necessary for observers to arise.” Davies also says that “the observed Universe is not minimally biophilic, and many scientists seem to think it is actually optimally biophilic.” I think he must be referring to the laws of physics and not necessarily all aspects of the universe being optimally biophilic.
Do we have indications from the fine-tuning of particle attributes that they are fine-tuned more than is strictly necessary to support life? Stephen Hawking seems to think so: “The summed quark masses seem roughly optimized for the existence of the largest number of stable nuclei.[12]” Many of these heavier elements are not essential to what would minimally count as a living observer but are important for technology and lead to a more bio-friendly universe. Multiverse theories generally entail new physics that predicts that protons decay. No one has yet seen such an event despite extensive attempts that allow us to compute a maximum possible proton decay rate. This decay rate turns out to be much greater than that predicted by the multiverse proposals. Nobel Prize-winner Frank Wilczek of MIT indicates that the lifetime of the proton is at least 10 orders of magnitude greater than necessary – this corresponds to a factor of ten billion.
Physicist Lee Smolin critiques multiverse theories because they fail to make predictions consistent with our universe. He notes that “there are constants that simply don’t have the values we would expect them to have if they were chosen by random distribution among a population of possibly true universes.[13]” Smolin points out the unexpected and unlikely relationship between quark and lepton masses. He further argues that under randomly varying laws, “some symmetries of elementary particles would be violated by the strong nuclear force much more than they are.[14]”
Another powerful example of fine-tuning that goes beyond what is strictly necessary for life can be seen in the properties of water. A 2011 article[15] from New Scientist highlighted research by scientists from Stanford and the Argonne National Lab:
“Water’s life-giving properties exist on a knife-edge. It turns out that life as we know it relies on a fortuitous, but incredibly delicate, balance of quantum forces. Water is one of the planet’s weirdest liquids, and many of its most bizarre features make it life-giving.” Consider just a few of the examples of the bio-friendly properties of water that are exceptional compared to other liquids:
- Higher density as liquid than solid (ice floats)
– Prevents lakes from freezing bottom up
– Ice at top then acts as a much better insulator than water to minimize additional freezing
- Very high heat capacity
– Moderates temperatures at global and organismal levels
- Latent heat of evaporation by far higher than other substances
– Increased ability to cool organisms
– Water’s unusually high thermal conductivity for a liquid also aids in cooling
- Unusually high surface tension
– Maximizes capillary action
- Low viscosity increase rate of diffusion, recycling of nutrients globally, and allows tiny capillaries (3 micron, single-cell thick wall) to nourish muscles
- Non-Newtonian fluid
– 2x increase in pressure leads to 3x rate of (blood) flow
- Viscosity of ice maximizes glacial activity
- Near universal solvent – great for transport within cells or recycling nutrients within an ecosystem
The article explains that fine-tuning was needed for water to have such properties: “computer simulations show that quantum mechanics nearly robbed water of these life-giving features… Water fortuitously has two quantum effects which cancel each other out… ” The article concludes: “We are used to the idea that the cosmos’s physical constants are fine-tuned for life. Now it seems water’s quantum forces can be added to this ‘just right’ list’.” The parameter at the most fundamental level that is finely-tuned is simply Planck’s constant since that affects the magnitude of the effects of Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle. However, recall that I mentioned previously that all of the force strengths have a term for Planck’s constant in them. Thus, Planck’s constant is independently highly constrained based on force strengths and yet this just happens to also result in water having all of these amazing and unusual properties that benefit life in a manner beyond what is explicable by multiverse theories.
An example of additional fine-tuning required under multiverse theories relates to the number of spatial dimensions. Theories that entail multiverses with differing parameters per universe generally predict additional spatial dimensions that have to be compactified if life is to exist because otherwise there would be neither stable atoms nor stable planetary orbits. A much more significant example of an additional fine-tuning is required by what seems to be the most popular multiverse theory, eternal inflation. I mentioned in an earlier blog but it’s worth repeating that Sean Carroll[16] and others have calculated that “inflation only occurs in a negligibly small fraction of cosmological histories, less than 10-66,000,000.” Thus, the multiverse isn’t very successful at explaining these finely-tuned parameters and the multiverse itself requires fine-tuning. The hypothesis of design therefore better explains the totality of the physics data.
[1] Leonard Susskind. The Cosmic Landscape, p. 176.
[2] As I’ve previously pointed, John von Neumann proved that information storage and replication are necessary for any type of life since life is a self-replicating system.
[3] Stephen Hawking and Leonard Mlodinow. The Grand Design, p. 160
[4] Barnes, p. 42-44.
[5] Barnes, p.48.
[6]Susskind, p. 176.
[7] Susskind, p. 174-5.
[8] Barnes, p. 44.
[9] Carr and Rees, “The Anthropic Cosmological Principle and the Structure of the Physical World,” Nature 278 (1979): 612.
[10] Susskind, p. 250. (The partner of the electron, the so-called selectron, would ruin chemistry.)
[11] Barnes, Luke. The Fine-Tuning of the Universe for Intelligent Life. Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia, p. 53. http://arxiv.org/abs/1112.4647
[12] Hawking and Mlodinow, p. 160.
[13] Lee Smolin. The Trouble with Physics: The Rise of String Theory, the Fall of a Science, and What Comes Next, p. 166.
[14] Smolin, p. 167
[15] Lisa Grossman. “Water’s quantum weirdness makes life possible.” New Scientist. 25 Oct, 2011. http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg21228354.900-waters-quantum-weirdness-makes-life-possible.html
[16]Carroll, Tam. Unitary Evolution and Cosmological Fine-Tuning. http://arxiv.org/abs/1007.1417v1