By Ryan Leasure
This is part three of a nine-part series on how we got our Bible. Part one addressed the inspiration and inerrancy of Scripture. Part two explained the formation and preservation of the Old Testament text. This post will address issues surrounding the Old Testament canon and the Apocrypha.
Canon
Before going any further, we must first establish what we mean when we say “canon.” We are not, of course, referring to the weapons of bygone eras. Rather, canon refers to an ancient measuring stick cut from a reed-like plant which was used as an infallible standard—much like a yardstick. The term was later applied to the biblical texts that the church received in its collection of authoritative books.
The Tanakh
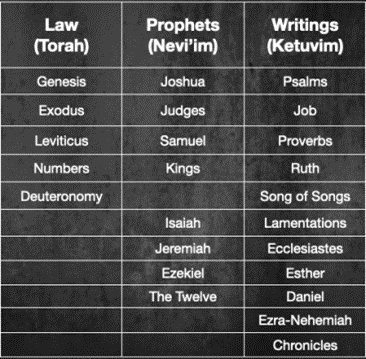
The Jewish order of the Old Testament was and is radically different from how we typically order our books. From an early time, it appears that the Jews had a threefold division of the Hebrew canon. This threefold division is often referred to as the Tanakh based on the three divisions—Torah (Law), Nevi’im (Prophets), and Ketuvim (Writings). This final division could sometimes be called “the Psalms” since Psalms was the first and largest book among the writings and was often representative of the whole. Also, note that Jews combined several books. So while their canon contains the same content as our protestant Bibles, their Bible only has twenty-four books instead of thirty-nine. Consider the breakdown below from Genesis to Chronicles:
The Septuagint (250-150 BC)
After Alexander the Great Hellenized the known world, Jewish scholars realized they needed to translate the Hebrew scriptures into Greek so that more people could read them. Legend has it that seventy-two Jewish translators (six from each of the twelve tribes), over the course of seventy-two days, each translated the text from Hebrew to Greek independently, and all seventy-two translations came out the exact same. The translation, therefore, came to be known as the Septuagint (from the Latin septuaginta meaning “seventy”) and is often represented by the Roman numerals LXX.
A couple of points are worth noting about the Septuagint. First, this translation changed the order of the books to the order that we are more familiar with today. That is to say, it changed from the threefold division of the Tenakh to our current order of law, history, poetry, major prophets, and minor prophets. Furthermore, the Septuagint also included the Apocrypha.
The Apocrypha
The Apocrypha consists of a dozen or so Jewish books written during the intertestamental period. These books contain history, poetry, wisdom literature, and prophecy. Probably most famous among the Apocrypha are the first and Second Maccabees. These books detail the Jewish rebellions and reclamation of the temple from the Syrians. While these works contain much historical value, they also contain disputable material. This is especially true of second Maccabees which teaches that saints in heaven intercede for people on earth (15:11-16) and that prayers and sacrifices can be offered for the dead (12:39-46). Roman Catholics us this last text to justify belief in purgatory and the practice of indulgences.
Tobit, another Apocryphal book, contains a fanciful story about a devout Jewish man in exile who is blinded by bird droppings in his sleep. His wife Sarah, also had troubles of her own. A demon had killed seven of her previous husbands on her wedding night. So God sent the angel Raphael to help Tobit and Sarah conquer the demon. Ultimately, they use a fish heart and liver to drive out the demon from the wedding chamber. Finally, Tobit’s son rubs fish gall on Tobit’s eyes to heal his blindness. This story is entirely fanciful.
Another book, known as Judith, describes God’s deliverance of the Jewish people. In this story, Judith seduces an Assyrian king only to cut off his head during his drunken stupor. We have no evidence that this story ever occurred. Moreover, this book erroneously states that Nebuchadnezzar was king of Assyria, not Babylon.
Other Apocryphal books include Sirach (wisdom literature similar to Proverbs), Baruch (not written by Baruch), Wisdom of Solomon (not written by Solomon), and additions to Daniel (Susanna and Bel and the Dragon).
Why The Bible should not Include the Apocrypha
You are probably familiar with the Protestant/Catholic/Orthodox debates over whether the Apocrypha belongs in our modern Bibles. In the remaining space, I’d like to offer five reasons why I don’t believe the Bible should include the Apocrypha.
1. The Apocrypha Acknowledges that Prophets Weren’t Speaking during its Time
Consider the following texts from 1 Maccabees:
So there was great distress in Israel, the worst since the time when the prophets ceased to appear among them (1 Macc. 9:27).
The Jews and their priests have resolved that Simon should be their leader and high priest forever, until a trustworthy prophet should arise (1 Macc. 14:41).
And laid up the stones in the mountain of the temple in a convenient place, until there should come a prophet to show what should be done with them (1 Macc. 4:46).
Notice how all three of these verses indicate God was not speaking through prophets during their time.
2. Jews Never Accepted the Apocrypha as Scripture
Consider the following quotation from first-century Jewish historian Josephus:
From the death of Moses to the time of Artaxerxes, who was king of Persia after Xerxes, the prophets who followed Moses have written down in thirteen books the things that were done in their days. The remaining four books contain hymns to God and principles of life for human beings. From Artaxerxes to our own time a detailed record has been made, but this has not been thought worthy of equal credit with the earlier records because there has not been since then the exact succession of prophets.1
Josephus indicates that after the time of Artaxerxes (465-424 BC), Jews continued to write books (the Apocrypha), but these books were not on par with Scripture, because the prophets had stopped speaking.
Moreover, the Babylonian Talmud, which is a sacred collection of Rabbinical traditions, notes that “after the latter prophets Haggai, Zechariah, and Malachi had died, the Holy Spirit departed from Israel” (Yoma 98). In other words, special revelation ceased after the time of these prophets. Therefore, we should not consider the Apocrypha as Scripture since it followed after these prophets.
Finally, around the year AD 90, a council of Jewish leaders gathered at Jamnia to figure out how to reconstruct Judaism after the fall of Jerusalem and the temple. As they discussed their sacred books, they merely reaffirmed the universal practice of all Jews that the Apocrypha did not belong in their Bible.
3. The New Testament Never Refers to the Apocrypha as Scripture
The New Testament authors quote from the Old Testament hundreds of times. Often they preface their quotes with phrases such as “it is written” or “Scripture says.” Consider the following examples:
As it is written: None is righteous, no, not one (Rom 3:10).
Scripture says, They will look on him whom they have pierced (John 19:37).”
Therefore, as the Holy Spirit says, Today, if you hear his voice, do not harden your hearts as in the rebellion (Heb 3:7-8).
Never once do the New Testament authors do something similar with an Apocryphal text. This omission is telling considering the fact that the New Testament authors usually quoted from the Septuagint which contained the Apocrypha. Meaning, the New Testament authors were well aware of the Apocryphal texts. They simply never refer to them as Scripture.
4. Jesus Affirmed the Three-Fold Division of the Tanakh
Two quotations from Luke indicate that Jesus believed in a closed Old Testament Canon that did not include the Apocrypha. Consider Luke 24:44:
Then he said to them, ‘These are my words that I spoke to you while I was still with you, that everything written about me in the Law of Moses and the Prophets and the Psalms must be fulfilled.
In this text, Jesus makes a clear affirmation of the threefold division of the Old Testament—Apocrypha not included. Also consider Luke 11:51:
From the blood of Abel to the blood of Zechariah, who perished between the altar and the sanctuary. Yes, I tell you, it will be required of this generation.
By speaking of Abel (the first biblical martyr) and Zechariah (the last biblical martyr), Jesus indicates that the Old Testament canon concluded with Chronicles (traditional order of the Tanakh). It is worth noting that several martyrs died in the Maccabees. Jesus doesn’t mention them because he didn’t consider Maccabees as part of his Bible.
5. The Catholic Church didn’t Grant Authority to the Apocrypha until Later
The earliest Old Testament canonical list from a Christian comes from Melito of Sardis (AD 170). His canon leaves out the Apocrypha. Origen’s canonical list in the mid-third century also leaves out the Apocrypha. Additionally, Athanasius, Cyril of Jerusalem, Gregory of Nazianzus, and the Council of Laodicea leave the Apocrypha out of their canon.
Sometime in the fourth century though, the Apocrypha started to gain acceptance in some circles as demonstrated by some of the canonical lists (St. Augustine and the Council of Hippo) and biblical manuscripts (Codex Sinaiticus and Vaticanus). Of course, St. Augustine also persuaded his friend Jerome to include the Apocrypha in the Latin Vulgate in AD 404. That said, Jerome prefaced the Apocryphal writings by stating:
Therefore as the church indeed reads Judith, Tobit, and the books of Maccabees, but does not receive them among the canonical books, so let it also read these two volumes for the edification of the people but not for establishing the authority of ecclesiastical dogmas.2
Jerome made a clear delineation between Scriptural texts and the Apocrypha. Scripture established church doctrine. The Apocrypha was for mere edification alone.
For the next thousand years, the Catholic Church was hardly unified on the Apocrypha. William of Ockham, influential medieval theologian, echoed Jerome’s sentiments when he wrote that apocryphal texts “are read for the edification of the people, but not for the establishment of doctrine.3 Even Cardinal Cajetan, a chief opponent of the Protestant Reformers and appointee of Pope Leo remarked:
The Latin church is greatly indebted to Jerome on account of his separation of the canonical from the uncanonical books. . . . those books and any others there may be like them in the Canon of the Bible are not canonical in the sense of establishing point of faith; yet they can be called canonical for the edification of the faithful.4
Despite being far from unified, the Council of Trent official granted canonical status to the Apocryphal text in what can only be seen as a counter-Reformation move.
Moving On to the New
The next post will transition to the New Testament. Specifically, the post will address two key question. First, would the early church have expected more Scriptural books? And second, what clues tipped off the early church that certain books were authoritative Scripture while others were not?
Recommended resources related to the topic:
Cold-Case Christianity: A Homicide Detective Investigates the Claims of the Gospels by J. Warner Wallace (Book)
Why We Know the New Testament Writers Told the Truth by Frank Turek (mp4 Download)
The Top Ten Reasons We Know the NT Writers Told the Truth mp3 by Frank Turek
Counter Culture Christian: Is the Bible True? by Frank Turek (Mp3), (Mp4), and (DVD)
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Ryan Leasure holds a Master of Arts from Furman University and a Masters of Divinity from the Southern Baptist Theological Seminary. Currently, he’s a Doctor of Ministry candidate at the Southern Baptist Theological Seminary. He also serves as a pastor at Grace Bible Church in Moore, SC.
Original Blog Source: https://cutt.ly/NY40j0n