[Editor’s Note: In part 1 of this series, Jonathan McLatchie introduced the book of Acts for it’s miracle accounts and the evidential value they carry. He argues that at least some of these miracles cannot be rationally dismissed out of hand but rather carry demonstrable evidential value for understanding the events of biblical history. McLatchie began by focusing on the miracles of the Apostle Paul. In Part 2, we pick up with more Pauline miracles.]

Striking Elymas Blind:
Acts 13:4-12 recounts Paul’s and Barnabas’ encounter with a magician by the name of Bar-Jesus, also called Elymas, on the island of Cyprus. Luke indicates that “he was with the proconsul, Sergius Paulus, a man of intelligence, who summoned Barnabas and Saul and sought to hear the word of God,” (v. 7). Elymas, however, “opposed them, seeking to turn to the proconsul away from the faith,” (v. 7). In response,
“[Paul] looked intently at him and said, ‘You son of the devil, you enemy of all righteousness, full of all deceit and villainy, will you not stop making crooked the straight paths of the Lord? And now, behold, the hand of the Lord is upon you, and you will be blind and unable to see the sun for a time.’ Immediately mist and darkness fell upon him, and he went about seeking people to lead him by the hand,” (v. 10-11).
So convincing is this miracle that it results in the conversion of the Proconsul, Sergius Paulus (v. 12). If indeed this episode represents the testimony of Paul, it is an episode about which it would have been difficult for Paul to be sincerely mistaken.
One specific detail that Luke gets right is that Cyprus was under the governorship of a Pronconsul. At the time of Paul’s journey (47-48 C.E.), there were about 12-15 senatorial provinces (which were under the governorship of a Proconsul), compared to a larger number of imperial provinces (which were under the governorship of legates, who were directly under the emperor’s control). Senatorial provinces were considered to be more peaceful and civilized, and therefore did not require troops to maintain the peace. Imperial provinces, on the other hand (such as Judea) had a standing military presence. Cyprus became a senatorial province in 22 B.C.E., meaning it was governed by a Proconsul instead of a legate or prefect (Cassius Dio, Historiae Romanae 54.4).[1] If Luke was simply making up details with no connection to actual events, it would have been easy for him to mistakenly call the governor a legate or to use some generic title. In fact, the evidence suggests that, by the time of the Flavian dynasty (commencing in 69 C.E. with the emperor Vespasian), Cyprus was transferred back to imperial control and under the authority of legates. If Acts were composed after 70 C.E., as many scholars maintain, it would have been even easier for Luke to err at this point. In an age before the internet and ease of access to information, small points of specialized local knowledge, such as this, evince the credibility of the account in Acts, since it would be significantly easier to get those details wrong than it would be to get them right. Details such as this would not be in the stock of common knowledge across the empire (see my essay here for a discussion of the significance of this type of evidence).
Another remarkable confirmation of the account in Acts is the identification of the Proconsul as Sergius Paulus. A Greek inscription of Soloi, on the northeast coast of Cyprus, is dated “in the Proconsulship of Paulus.” This inscription is shown in the photograph below:
 Though we cannot say for certain, it is quite plausible that this is the same individual spoken of in Acts. Though the precise date of the inscription is uncertain, it likely belongs to the first century C.E. This individual is said to have served as Proconsul during the tenth year of an emperor, though the name is missing from the inscription. Ben Witherington notes, “If the emperor in question was Claudius, the inscription would date to about A.D. 50, but the very date line seems to be a later addition. It thus remains possible that this refers to the same Sergius Paulus as mentioned in Acts, but it is also possible on epigraphical grounds that the inscription comes from as late as the time of Hadrian in the second century.”[2] Nonetheless, regardless of whether this is the same individual or not, the inscription demonstrates a connection of the family to the island of Cyprus, consistent with the account in Acts.
Though we cannot say for certain, it is quite plausible that this is the same individual spoken of in Acts. Though the precise date of the inscription is uncertain, it likely belongs to the first century C.E. This individual is said to have served as Proconsul during the tenth year of an emperor, though the name is missing from the inscription. Ben Witherington notes, “If the emperor in question was Claudius, the inscription would date to about A.D. 50, but the very date line seems to be a later addition. It thus remains possible that this refers to the same Sergius Paulus as mentioned in Acts, but it is also possible on epigraphical grounds that the inscription comes from as late as the time of Hadrian in the second century.”[2] Nonetheless, regardless of whether this is the same individual or not, the inscription demonstrates a connection of the family to the island of Cyprus, consistent with the account in Acts.
There is another interesting inscription that was identified in Pisidian Antioch, shown below.
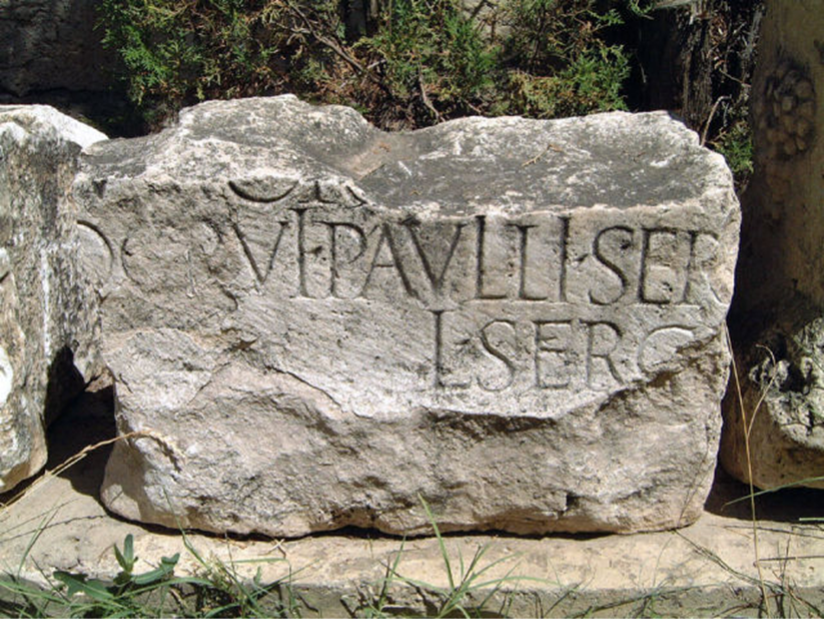

This inscription bears the name of “L. Sergius Paullus the younger, son of L.” (note that Paullus is the Latin spelling, whereas Paulus is the Greek spelling). It is probable that “L” stands for Lucius, given the limited number of commonly used first names among Roman men. The inscription reads, “To L(ucius) Sergius Paullus, the younger, son of L(ucius), one of the four commissioners in charge of the Roman streets, tribune of the soldiers of the sixth legion styled Ferrata, quaestor…” It has even been suggested that this could be the son, or another relative, of the Proconsul mentioned in Acts. Given the connection of this individual to Pisidian Antioch, is it a coincidence that Paul and Barnabas travelled to Pisidian Antioch immediately following these events, after Sergius Paulus’ conversion to Christianity? Pisidian Antioch was not the nearest or most obvious stop after Cyprus. It is plausible that Sergius Paulus convinced Paul to travel to Pisidian Antioch with a desire for his relatives there to hear the gospel.
These connections to the archaeological evidence strongly suggest that the account in Acts 13:4-12, in which Paul causes Bar-Jesus (Elymas) to go blind in response to his opposition to the gospel, represents the testimony of Paul himself.
Healing the Cripple at Lystra:
In Acts 14:8-10, we read,
“Now at Lystra there was a man sitting who could not use his feet. He was crippled from birth and had never walked. 9 He listened to Paul speaking. And Paul, looking intently at him and seeing that he had faith to be made well, 10 said in a loud voice, ‘Stand upright on your feet.’ And he sprang up and began walking.”
In this account, Paul miraculously heals a man in Lystra who had been crippled since birth, a feat which greatly impresses the crowds. Verse 11 indicates that, “when the crowds saw what Paul had done, they lifted up their voices, saying in Lycaonian, ‘The gods have come down to us in the likeness of men!’” Luke indicates that this was said in the Lycaonian language. The use of a native language, rather than Greek, was quite uncommon. Colin Hemer notes that “The use of a native language is unusual in the cosmopolitan, Hellenized society in which Paul moved. Lystra, however, as a Roman colony in a less developed part of Anatolia, preserved a language otherwise attested in a gloss in Stephanus of Byzantium.”[3] While Greek was widely spoken in urban centers and among the elite, rural populations (particularly in more isolated areas) retained their native tongue. This is, therefore, a specific (and unusual) local detail about Lycaonia that Luke gets right.
According to verse 12, “Barnabas they called Zeus, and Paul, Hermes, because he was the chief speaker.” A number of inscriptions have been identified that confirm that Zeus-Hermes was the local cult in Lystra. The first century Roman poet Ovid writes, in his poem Metamorphoses, about Zeus and Hermes visiting a town in Phrygia, disguised as mortals seeking hospitality.[4] Only an elderly couple, Baucis and Philemon, welcome them, and as a reward for their kindness, the gods transform their humble home into a temple and grant them their wish to die together. Phrygia and Lycaonia were both located in central Anatolia (modern day Turkey) and the story of Baucis and Philemon is generally thought to be set close to the border with Lycaonia. This is, therefore, another specific local detail that Acts gets right. The fact that Barnabas is identified as Zeus (the greater of the two gods), whereas Paul is identified as Hermes also reflects the ancient belief that, when two deities visited earth, the lesser god did the speaking.
These specific details relating to Lystra, related accurately by Acts, suggests that the account of the healing of the crippled man reliably represents Paul’s testimony.
Paul’s Prison Break in Philippi:
In Acts 16, Paul and Silas, while in Philippi, cast out a spirit of divination from a slave girl. This leads to them being dragged into the marketplace before the rulers by the slave girl’s owners, and ultimately lands them in prison for causing a disturbance, their feet being fastened in stocks. At midnight, as they are praying and singing in the prison, there is a great earthquake, which shakes the foundations of the prison. The text tells us that “immediately all the doors were opened, and everyone’s bonds were unfastened,” (v. 26). The jailer is about to take his own life, but Paul cries out, “Do not harm yourself, for we are all here,” (v. 28). This ultimately leads to the conversion and baptism of the jailer and his household. In verses 35-40, we read,
“But when it was day, the magistrates sent the police, saying, ‘Let those men go.’ 36 And the jailer reported these words to Paul, saying, ‘The magistrates have sent to let you go. Therefore come out now and go in peace.’ 37 But Paul said to them, ‘They have beaten us publicly, uncondemned, men who are Roman citizens, and have thrown us into prison; and do they now throw us out secretly? No! Let them come themselves and take us out.’ 38 The police reported these words to the magistrates, and they were afraid when they heard that they were Roman citizens. 39 So they came and apologized to them. And they took them out and asked them to leave the city. 40 So they went out of the prison and visited Lydia. And when they had seen the brothers, they encouraged them and departed.”
Paul briefly alludes to this episode in a letter to the Thessalonians: “But though we had already suffered and been shamefully treated at Philippi, as you know, we had boldness in our God to declare to you the gospel of God in the midst of much conflict,” (1 Thess 2:2, emphasis added). This raises the question as to how the Thessalonians knew about Paul’s shameful treatment in Philippi. Turning to Acts 17:1, we read, immediately following Paul’s experience in Philippi, “when they had passed through Amphipolis and Apollonia, they came to Thessalonica.” The route taken by Paul was, in fact, a major Roman highway, the Via Egnatia. Amphipolis and Apollonia were overnight stops along that route. Paul’s route from Philippi to Thessalonica is depicted in the map below.
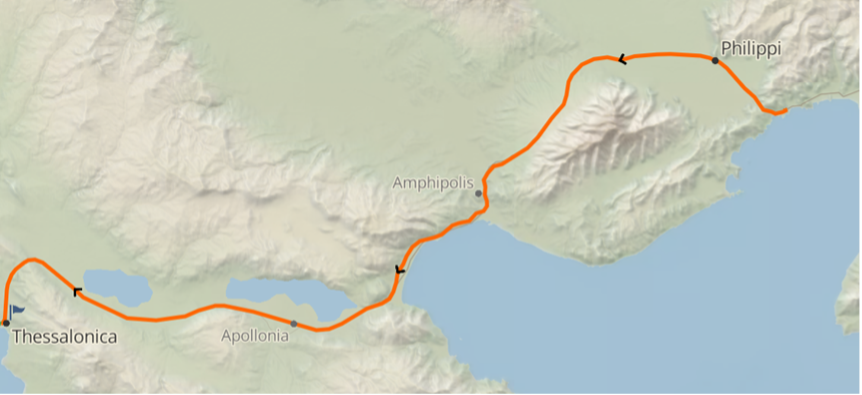
One can imagine, then, Paul arriving in Thessalonica having just come from Philippi, still full of indignation about the unjust and illegal treatment he had received there, and recounting to the new converts in Thessalonica what had happened. This dovetails with Paul’s allusion in 1 Thessalonians 2:2 to how he had “been shamefully treated at Philippi, as you know…”
The evidential force of this coincidence is enhanced by the fact that Acts does not appear to be utilizing 1 Thessalonians as a source — that is to say, these two writings are independent of one another. In support of this, it may be observed that 1 Thessalonians 1:9 emphasizes the conversion of pagans in Thessalonica: “. . . you turned to God from idols to serve the living and true God . . . ” The book of Acts, on the other hand, emphasizes the conversion of Jews and god-fearing gentiles (Acts 17:4). These are, of course, not mutually exclusive. Nonetheless, if the author of Acts were using 1 Thessalonians as a source, one would expect him to lay more emphasis on the conversion of pagans.
This undesigned coincidence provides evidence for the contention that the account of Paul’s prison break in Philippi, resulting from the earthquake, in fact represents Paul’s own testimony. The account is also linked to Paul having cast out a spirit of divination from the slave girl, which was the incident that led to his imprisonment along with Silas in Philippi.
The Raising of Eutychus:
Acts 20:7-12 recounts the raising of Eutychus, a young man who fell asleep during Paul’s sermon, and fell to his death from a third-story window. According to verse 9-10, “being overcome by sleep, he fell down from the third story and was taken up dead. But Paul went down and bent over him, and taking him in his arms, said, ‘Do not be alarmed for his life is in him.’” The word νεκρός, used in this text, refers to a literal death rather than merely a lack of consciousness. Though some have disputed that Luke intended to convey that Paul raised Eutychus from the dead, and have asserted instead that Paul simply recognized vital signs in Eutychus, this is not the plainest reading. Ben Witherington observes,
“Though there has been considerable debate, v. 9b does say he was picked up dead; the text does not say it appeared as if he was dead (contrast 14:19). In short, in what follows we have a miracle tale about the raising of the dead, following the usual form of such a tale with the confirmation of the cure and the reaction of the observers at the very end of the narrative.”[5]
Moreover, as a medical physician (Colossians 4:14), Luke would likely have been able to distinguish between someone who was dead and someone who was merely unconscious or in a coma. If Eutychus had been merely injured or in a deep faint, Luke probably would have noted that rather than describing him as “dead.”
Unlike the previously discussed miracles, Luke claims to have been witness to this miracle himself (verse 7). That Luke was indeed Paul’s travelling companion is borne out by numerous lines of evidence, both internal and external, which I will not unpack in detail here. Luke’s demonstrated track-record of historical scrupulousness also indicates that he was in the habit of being truthful. Moreover, Luke, in travelling with Paul amidst the persecutions that Paul experienced — including being present with Paul in Caesarea Maritima, where Paul was imprisoned for two years (Acts 24:27) and then again as Paul set sail for Rome to stand trial before Caesar (Acts 27-28) — put his neck on the line for the gospel. Paul indicates that Luke was present with him during his first imprisonment (Col 4:14; Philem 24) and again during his second imprisonment in Rome (2 Tim 4:11). This, again, evinces Luke’s sincerity.
The Miracles of Peter
Luke indicates that he was present with Paul in Jerusalem when Paul visited the elders of the Jerusalem church (Acts 21:17-18). Luke mentions James, Jesus’s brother, by name, and indicates that “all the elders were present,” (v. 18). According to Galatians 2:9, the leaders of the church in Jerusalem included James, as well as Simon Peter, and John the son of Zebedee. Luke was also present with Paul when Paul was imprisoned in Caesarea Maritima for at least two years (Acts 24:27), in relative geographical proximity to Jerusalem (a two or three day journey on foot). Luke would have presumably had ample access during this time to the apostles. He was, therefore, in a position to know what the apostles were claiming. Luke, moreover, indicates in his address to Theophilus, in the prologue to his gospel, that he was interested in the testimony of “those who from the beginning were eyewitnesses and ministers of the word.” The numerous points of specific confirmation of the gospel of Luke also indicate that Luke extracted reliable information from the apostles concerning Jesus’s ministry. Taken together, these considerations support that Luke had access to, and reliably represented, the apostles’ claims.
Peter in particular is reported to have performed various miracles that one could not readily be sincerely mistaken about (see those miracles performed, or experienced, by Peter in the list supplied at the beginning of this article). In addition to healing individuals who were lame (Acts 3:2-10) or paralyzed (Acts 9:33-34), he is alleged to have raised Dorcas from the dead, an incident which became known throughout all Joppa and resulted in many conversions (Acts 9:36-42). Peter also struck Ananias and Saphira dead at a word, as God’s judgment for having lied about the price obtained for their land, an incident that caused great fear to come upon the whole church (Acts 5:1-11). Furthermore, Peter experiences a miraculous prison break, where he is led out of the jail by an angel (Acts 12:6-11). There is also another incident where the apostles as a group are liberated from prison by an angel (Acts 5:18-20). The other apostles are also said to have performed many signs and wonders, healings and exorcisms, though no details are supplied (Acts 5:12-16).
The Miracles of Philip the Deacon
Luke indicates that he lodged at the house of Philip the deacon: “On the next day we departed and came to Caesarea, and we entered the house of Philip the evangelist, who was one of the seven, and stayed with him” (Acts 21:8). Thus, Luke was in a position to know what Philip himself claimed concerning his activities and alleged miracles. According to Acts 8:6-8,
“[T]he crowds with one accord paid attention to what was being said by Philip, when they heard him and saw the signs that he did. For unclean spirits, crying out with a loud voice, came out of many who had them, and many who were paralyzed or lame were healed. So there was much joy in that city.”
Moreover, Philip’s encounter with the Ethiopian Eunuch, in Acts 8:26-38, though not a miracle per se, is nonetheless an occasion of special providence, since the Ethiopian coincidentally happens to be reading Isaiah 53, a major text in the Hebrew Bible concerning the Messiah, which Philip is consequently able to explain to him (see my detailed essay on Isaiah 53 here). In Acts 8:39-40, we read of another miraculous event following the Ethiopian’s baptism: “And when they came up out of the water, the Spirit of the Lord carried Philip away, and the eunuch saw him no more, and went on his way rejoicing. But Philip found himself at Azotus, and as he passed through he preached the gospel to all the towns until he came to Caesarea.” The sudden transportation of Philip to Azotus, about twenty miles north of Gaza, is surely an event about which one could hardly be sincerely mistaken.
The Evidential Value of the Miracles in Acts
I have argued in the foregoing that the accounts in Acts concerning the miracles performed, and experienced, by Paul, Peter and Philip actually represent the testimony of those individuals. Given the nature of those alleged miracles, it is quite implausible that they could be sincerely mistaken. I have argued at length elsewhere that the context of persecution evinces the sincerity of Paul and the other apostles (see my article on this here). The miracles recorded in Acts, therefore, provide further support for the truth of Christianity.
References:
[1] Strabo, The Geography of Strabo. Literally Translated, with Notes, in Three Volumes., ed. H. C. Hamilton (Medford, MA: George Bell & Sons, 1903), 71–72.
[2] Ben Witherington III, The Acts of the Apostles: A Socio-Rhetorical Commentary (Grand Rapids, MI: Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co., 1998), 399–400.
[3] . Colin J. Hemer, The Book of Acts in the Setting of Hellenistic History, ed. Conrad H. Gempf (Winona Lake, IN: Eisenbrauns, 1990), 110.
[4] P. Ovidius Naso, Metamorphoses, ed. Arthur Golding (Medford, MA: W. Seres, 1567).
[5] Witherington 1998, Acts 20:9-10.
Recommended Resources:
Miracles: The Evidence by Frank Turek DVD and Mp4
Two Miracles You Take With You Everywhere You Go by Frank Turek DVD, Mp3 and Mp4
Why We Know the New Testament Writers Told the Truth by Frank Turek (DVD, Mp3 and Mp4)
Can All Religions Be True? mp3 by Frank Turek
Dr. Jonathan McLatchie is a Christian writer, international speaker, and debater. He holds a Bachelor’s degree (with Honors) in forensic biology, a Masters’s (M.Res) degree in evolutionary biology, a second Master’s degree in medical and molecular bioscience, and a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology. Currently, he is an assistant professor of biology at Sattler College in Boston, Massachusetts. Dr. McLatchie is a contributor to various apologetics websites and is the founder of the Apologetics Academy (Apologetics-Academy.org), a ministry that seeks to equip and train Christians to persuasively defend the faith through regular online webinars, as well as assist Christians who are wrestling with doubts. Dr. McLatchie has participated in more than thirty moderated debates around the world with representatives of atheism, Islam, and other alternative worldview perspectives. He has spoken internationally in Europe, North America, and South Africa promoting an intelligent, reflective, and evidence-based Christian faith.
Originally posted at: https://bit.ly/3G2VNtu