By Ryan Leasure
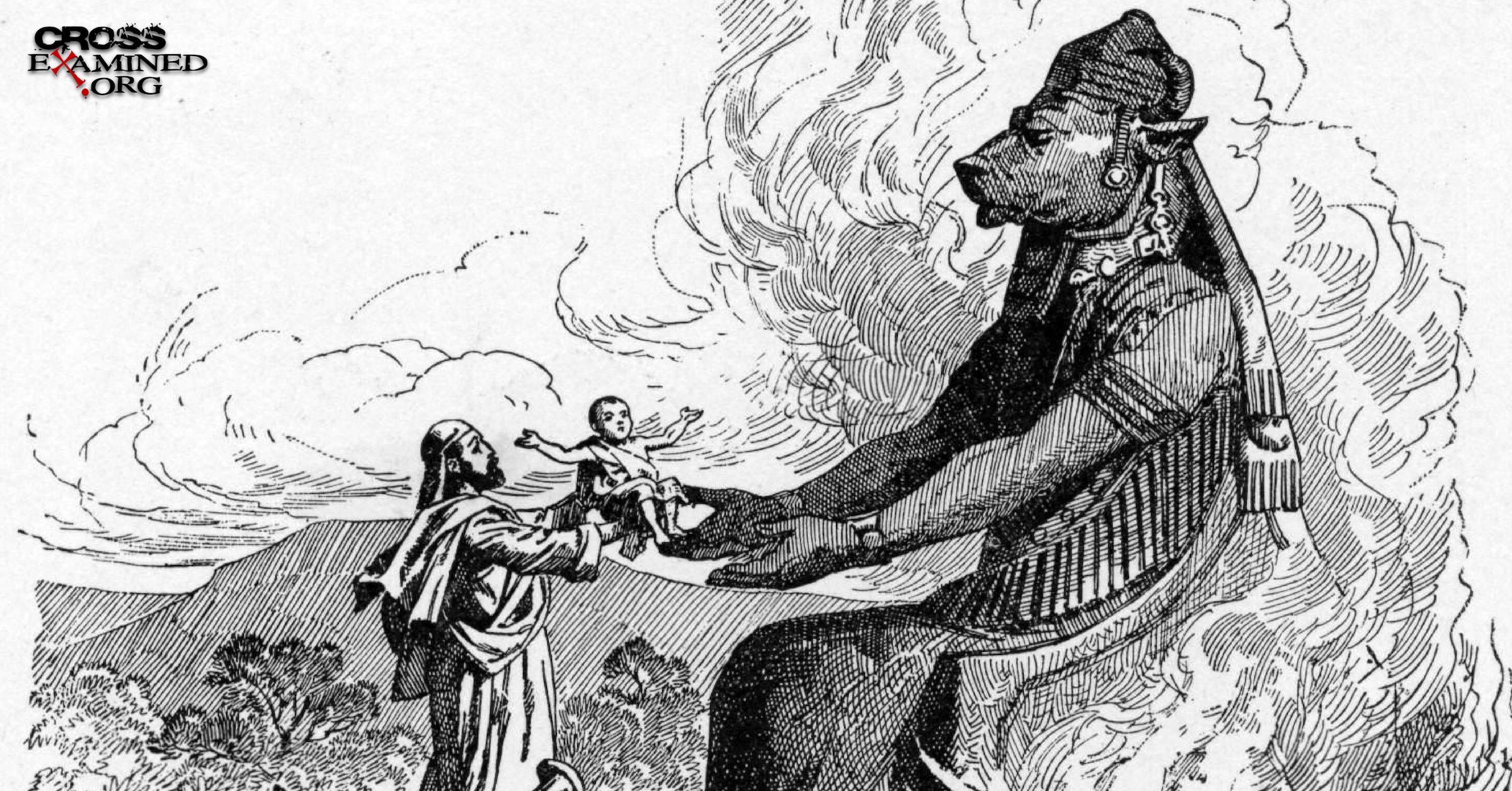
History is filled with barbaric cultures. One of the worst, though, has to be the ancient Canaanites. As was customary in that culture, parents offered their newborn children as sacrifices to their god Molech. Most depictions of Molech include large metal statues of a man with a bull’s head. Usually these statues had outstretched arms to hold the baby sacrifices.
During the sacrificial process, the Canaanites would light a fire inside or around the statue to heat up the statue as hot as they could. Then they would place their newborns into the red-hot arms of Molech and watch the children sizzle to death.
During this gruesome event, the Canaanites would play flutes and bang on drums to drown out the sound of their shrieking children. It’s truly awful stuff. No wonder God ordered the Israelites to destroy them.
Molech in The Bible
The Bible mentions Molech or at least references him about ten times. Here are a couple examples:
“Any Israelite or any foreigner residing in Israel who sacrifices any of his children to Molech is to be put to death. The members of the community are to stone him.” — Leviticus 20:2
“They built high places for Baal in the Valley of Ben Hinnom to sacrifice their sons and daughters to Molech, though I never commanded — nor did it enter my mind — that they should do such a detestable thing and so make Judah sin.” — Jeremiah 32:35
You might wonder why the Israelites would be tempted to sacrifice their children to Molech. As was the case with other ancient gods, Molech offered them some kind of benefit in exchange for their devotion. By offering up their children to be burned on the golden statue, the Canaanites believed Molech would cause them and their future children to prosper.
Our Molech Today
I don’t know a single person who hears about the horrors of Molech and doesn’t cringe at the gruesomeness. Brutally murdering babies in the name of Molech for future benefits is evil in the truest sense of the word.
Yet, at the same time, a large number of people today believe this ancient practice would be fine, so long as the baby was still in the womb. Just yesterday, New York legislators passed a law that allows for abortions up until birth. After the vote, this video circulated the internet showing hundreds of people cheering loudly in favor of this decision. It’s honestly one of the most disgusting scenes I’ve ever witnessed.
What kind of sick and twisted mind does one have to have to applaud the killing of unborn babies? These are babies after all. As I watched the video, I couldn’t help but think about the loud drums drowning out the babies’ screams.
“It’s Not as Bad as You Say It Is”
Since this new law allows women to abort their babies right before they go into labor, a woman can literally kill her baby one day and have people cheer for her, but if she kills her baby less than twenty-four hours later when it’s made it outside her womb, she’ll go to prison. It’s mind-blowing.
And let’s not pretend like the babies don’t feel a thing either. More studies than I can count demonstrate that babies at a very early stage can feel pain, not to mention taste food, hiccup, smile, dream, kick, and bond with their mother. So, when the abortion “doctor” injects the baby’s head with poison, know for sure the baby feels it and dies a horrifying death.
But they say, the law doesn’t allow for “any old abortion.” After all, the law says that only if the woman’s “life and health” are in jeopardy may she have an abortion up until birth.
The problem with this is that “health” could qualify for almost anything. It could mean physical health, but it could also mean psychological, mental, or financial health. In other words, it’s so vague that someone could get a late-term abortion for almost any reason. All the woman needs to say is that the baby would cause too much stress in her life because of added financial responsibilities, and she’s got her ticket to an abortion. Plain and simple.
Unborn Babies in The Old Testament
Though anyone with a first-grade knowledge of biology can see that a newborn and a full-term baby are scientifically the same, Christians have extra motivation to reject abortion because of Scripture’s clear teaching on the issue. Take Exodus 21:22-25 for example:
If people are fighting and hit a pregnant woman and she gives birth prematurely, but there is no serious injury, the offender must be fined whatever the woman’s husband demands and the court allows. But if there is a serious injury, you are to take life for life, eye for eye, tooth for tooth, hand for hand, foot for foot, burn for burn, wound for wound, bruise for bruise.
In short, no one should ever harm an unborn baby. If they do, the law calls for a strict penalty (life for life, eye for eye, etc.).
It’s interesting to note, that according to Old Testament law, accidentally killing someone did not result in “life for life.” Instead, accidental killers were sent to a city of refuge to stay away from the rest of the population (Num. 35:9-15). Meaning, God had an even stricter warning for accidentally killing unborn babies than people outside the womb.
Are you following the logic? If God had strict warnings against accidentally killing unborn babies, he must despise the fact that we kill them intentionally and then celebrate it to boot. So, when the mayor of New York lit up the World Trade Center in pink to celebrate more murder, we can rest assured that God doesn’t take it kindly. I mean, if that’s not a symbolic middle finger to God, I don’t know what is.
The Unborn Jesus
The birth of Jesus is a familiar one. The angel Gabriel appears to Mary and says that she’s going to conceive and give birth to a son. During her pregnancy, she visits her sister Elizabeth who was also pregnant at the time. Luke 1:41-44 reports:
When Elizabeth heard Mary’s greeting, the baby leaped in her womb, and Elizabeth was filled with the Holy Spirit. In a loud voice, she exclaimed: “Blessed are you among women, and blessed is the child you will bear! But why am I so favored, that the mother of my Lord should come to me? As soon as the sound of your greeting reached my ears, the baby in my womb leaped for joy.”
First, we notice that the text refers to the unborn child in Elizabeth’s womb as a baby (Greek, brephos). It’s the same Greek word used to describe children outside the womb (Lk. 18:15). And we see that this same baby was already able to recognize Jesus’ presence. In other words, he’s not just a lump of tissue.
Furthermore, Elizabeth, filled with the Holy Spirit, recognizes that Mary is the “mother of my Lord.” That is, she recognized Mary’s status as a mother despite the fact that Jesus was still in the womb.
While commenting on this text, Christian ethicist John Jefferson Davis writes:
The significant point is that God chose to begin the process of incarnation [in the womb], rather than at some other point, thus affirming the significance of that starting point for human life.1
Davis makes a good point. Since Jesus’ birth was miraculous, God could have chosen to start Jesus’ life at any point. He could have dropped him down from the sky and left him at someone’s doorstep. But instead, God chose to begin Jesus’ life in Mary’s womb demonstrating the value of unborn babies. I think we can all be glad that Mary didn’t have an abortion.
The Irony of Abortion
To date, Americans have slaughtered millions upon millions of unborn babies. Think about all those little innocent, vulnerable people, killed before they were even given a chance. And at the same time, we judge other nations for their less than humane practices. Who are we to talk?
But the greatest amount of irony is that every person in favor of abortion made it out of the womb alive. Every. Single. One. I dare say, they’re all grateful too.
Abortion and The God Molech
Truth is, we aren’t any better than the ancient Canaanites. Instead of sacrificing our children to the god Molech in exchange for future prosperity, we sacrifice our children in exchange for better career paths, financial security, and convenience.
While abortion apologists try to sanitize abortion by using terms like “tissue” instead of “baby” or “end the pregnancy” instead of “killing,” there’s no denying what’s going on when we inject poison into babies’ heads. We’re brutally murdering them. And we’ve done it millions of times. Lord, have mercy on us.
Ryan Leasure holds an M.A. from Furman University and an M.Div. from the Southern Baptist Theological Seminary. He currently serves as a pastor at Grace Bible Church in Moore, SC.
Original Blog Source: http://bit.ly/2RrBrea